AI in manufacturing: Use cases, solution, implementation and applications of AI agents
The manufacturing industry has long faced various challenges, including process inefficiencies, production errors, and costly machine maintenance. These issues stem from inefficiencies in manual processes, human errors, and a lack of real-time insights, resulting in escalated expenses, compromised quality, and missed opportunities. One of the primary obstacles manufacturing plants face is accurately detecting faults in the production process. Traditional methods often rely on simplistic procedures that fail to identify and resolve production issues effectively. However, Artificial Intelligence (AI) presents a promising way to address these challenges.
By harnessing AI’s capabilities, manufacturing companies can overcome hurdles such as fault detection, error reduction, and maintenance optimization. AI’s capacity to learn from vast datasets can significantly enhance the precision and efficiency of production cycles, diminishing the need for manual intervention in the manufacturing sector. Moreover, AI-powered analytics equip organizations with the tools that enable them to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance inventory management. As per Precedence Research, the global market for AI in manufacturing reached a value of USD 3.8 billion in 2022. It is projected to attain approximately USD 68.36 billion by 2032, experiencing a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.5% from 2023 to 2032.
This article discusses the significance of AI in the manufacturing industry, exploring compelling AI use cases in manufacturing that exemplify its potential to drive operational excellence and propel the industry toward new horizons.
- What is AI in manufacturing?
- AI in manufacturing: Use cases across various departments
- AI use cases in manufacturing
- Market trends research
- Identifying consumer preferences
- Historical data analysis
- Innovation and ideation
- Materials research
- Designing
- Defect detection
- Assembly line integration
- Predictive analytics
- Real-time monitoring and analysis
- Process optimization
- Energy management
- Supply chain optimization
- Demand forecasting
- Warehouse management
- Fair compensation management
- Reporting
- Personalization
- Email marketing
- Copywriting
- Yield optimization and batch analysis
- Smart energy management
- Order management
- Additive manufacturing
- Reading text and barcodes with OCR
- Digital twin simulations
- Wearable technologies for workplace safety
- Production scheduling and management
- Managing purchasing price variance
- Cybersecurity
- How LeewayHertz’s advanced generative AI platform optimizes manufacturing processes
- LeewayHertz’s AI development services for manufacturing
- How does AI address key challenges across every step of the manufacturing workflow?
- How can AI be implemented in the manufacturing workflow for enhanced efficiency and innovation?
- Ethical considerations in the deployment of AI within the manufacturing sector
- AI in manufacturing: Key technologies and techniques
- Benefits of AI in manufacturing
- Leveraging AI agents for optimizing manufacturing processes for quality and efficiency
- Future trends and opportunities
What is AI in manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing is the implementation of artificial intelligence technologies in the manufacturing industry to enhance efficiency, productivity, and decision-making processes. This includes using AI for tasks such as predictive maintenance, quality control, process optimization, supply chain management, robotics automation and more. AI algorithms analyze large volumes of data from sensors and other sources to make intelligent decisions and streamline manufacturing processes.
With AI-powered automation, manufacturers can automate iterative tasks, freeing up human resources to concentrate on more complex and strategic activities. This increases productivity and improves the overall efficiency of manufacturing operations. As per reports by Capgemini, the US ranks third in employing AI in manufacturing sector.
AI in manufacturing: Use cases across various departments
In the contemporary landscape of manufacturing, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changing force, propelling the industry into new realms of efficiency, precision, and innovation. From streamlining processes to optimizing resource allocation, AI’s applications within different departments of a manufacturing business are redefining the way operations are conducted. Here is an overview of diverse use cases of AI within each department.
Research and Development (R&D)
In research and development, AI enhances product development through predictive analytics. By analyzing market trends, consumer preferences, and historical data, AI algorithms can predict the demand for new products, enabling companies to focus their R&D efforts more strategically. Additionally, AI-powered simulations facilitate the creation of prototypes and virtual testing, accelerating the innovation cycle.
Production and operations
AI’s influence in the production department is profound, ranging from predictive maintenance to quality control. Smart sensors and IoT devices combined with AI algorithms can predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules. AI-powered machine vision systems ensure stringent quality control by identifying defects and inconsistencies in real-time, resulting in fewer defects and higher product quality.
Supply chain and logistics
Efficiency in the supply chain is greatly enhanced by AI-powered demand forecasting and inventory optimization. AI algorithms analyze historical data, seasonality, and external factors to predict demand patterns accurately, enabling manufacturers to maintain optimal inventory levels and reduce stockouts. Route optimization algorithms also enhance logistics, minimizing transportation costs and delivery times.
Human resources and workforce management
AI-driven solutions are redefining workforce management. AI-powered chatbots streamline recruitment processes by screening resumes and conducting initial interviews. Employee engagement is improved through sentiment analysis, identifying potential issues and addressing them proactively. Predictive analytics aid in workforce planning, helping manufacturers allocate human resources optimally to meet production demands.
Sales and marketing
AI is transforming sales and marketing by enabling personalized customer experiences. Customer data is analyzed to create targeted marketing campaigns, improving customer engagement and conversion rates. Predictive analytics assist in identifying potential leads, while AI-driven chatbots provide real-time customer support, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Finance and cost management
In the financial department, AI plays a pivotal role in cost management. Predictive analytics optimize procurement processes, ensuring the procurement of materials at the right time and price. AI algorithms monitor expenses, identifying areas where cost-saving measures can be implemented, thus contributing to overall operational efficiency.
Payroll
Efficient payroll management is vital for the smooth operation of a manufacturing unit. Its core objectives include timely compensation of employees, adherence to payroll tax deadlines, and the accurate calculation of wages based on attendance, shift schedules, and hours worked. To achieve these goals, HR departments often rely on advanced AI attendance management systems as a crucial tool for seamless operations. AI aids in this process by automating attendance tracking through advanced biometric or facial recognition systems, reducing errors and streamlining payroll calculations. It can also provide insights into attendance patterns and help predict potential scheduling issues, allowing for proactive workforce management and cost savings.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
AI use cases in manufacturing
In the contemporary landscape of manufacturing, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a game-changing force, propelling the industry into new realms of efficiency, precision, and innovation. From streamlining processes to optimizing resource allocation, AI’s applications within different departments of a manufacturing business are redefining the way operations are conducted. Here are some diverse AI use cases in manufacturing:
Market trends research
AI aids market trends research in manufacturing by analyzing vast data sets to identify patterns and emerging trends. It can predict consumer demand, optimize supply chains, and enhance product development by extracting valuable insights from structured and unstructured data. AI-driven analytics help research departments make data-driven decisions, improve forecasting accuracy, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can automate data collection and analysis, saving time and resources for research teams.
Identifying consumer preferences
AI aids the manufacturing research department by analyzing vast consumer preferences datasets, including online reviews, social media comments, and purchasing history. Machine learning algorithms can identify trends, sentiment, and emerging preferences, helping manufacturers make data-driven decisions on product design, features, and marketing strategies. This enables them to meet evolving consumer demands more effectively, reduce product development cycles, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction and product success.
Historical data analysis
AI aids historical data analysis in manufacturing research by automating data extraction, cleansing, and organization, allowing researchers to access past records efficiently. ML models can identify patterns and anomalies in historical data, helping researchers make informed decisions and optimize processes. Predictive analytics can forecast future trends based on past data, enabling proactive decision-making. Natural language processing (NLP) can also assist in mining insights from textual historical documents, enhancing research capabilities in manufacturing departments.
Innovation and ideation
AI’s role in fostering innovation and ideation within the manufacturing sector is pivotal, enabling the sector to analyze extensive datasets to pinpoint emerging trends, discern market needs, and understand competitor approaches. By drawing insights from varied data sources like scholarly articles, intellectual property documents, and consumer feedback, AI serves as a catalyst for the development of novel ideas and resolutions. Moreover, AI-driven predictive analytics assist in anticipating possible risks and refining resource distribution for research endeavors, enabling enlightened decision-making and propelling innovation. In this manner, AI is not just a tool but a strategic partner, driving forward-thinking and innovative solutions in manufacturing.
Materials research
AI facilitates materials research in the manufacturing sector by optimizing resource utilization. It helps determine the precise amount of materials required for a given application, reducing waste and enhancing sustainability. AI technologies can expedite the process of discovering new materials by predicting their properties using existing data, which can significantly conserve time and resources in research and development. This enables researchers to focus more on innovation and development of new materials rather than spending extensive time on testing and analyzing every potential new material, optimizing the overall R&D process in material science. Simulations using AI-driven models can simulate material behavior under different conditions, aiding in the development of new materials.
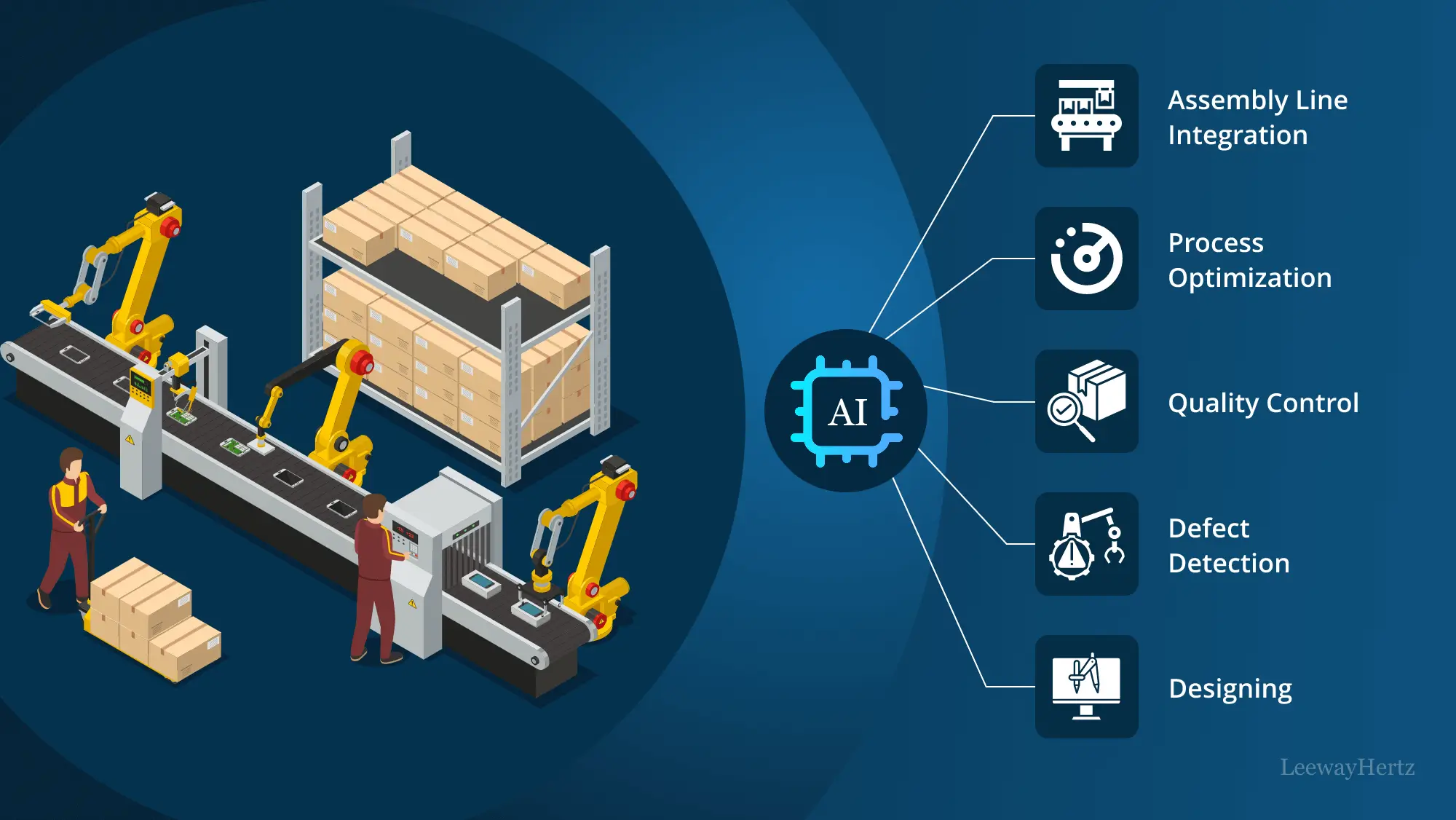
Designing
AI plays a vital role in manufacturing by aiding in the design process. It leverages advanced algorithms to analyze extensive datasets and simulate various design scenarios, enabling engineers to optimize product designs for performance, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. Machine learning algorithms can also generate innovative design ideas by identifying patterns and trends that humans might overlook. Additionally, AI-driven design tools enhance collaboration by providing real-time feedback and automating repetitive tasks, ultimately accelerating the product development cycle and fostering innovation in manufacturing.
Defect detection
Many assembly lines lack effective defect detection systems, often relying on basic setups that require skilled engineers to manually program. These systems generate many false alarms, leading to time-consuming manual checks. By adding artificial intelligence and self-learning capabilities, manufacturers can save time and reduce false alarms, improving efficiency.
Assembly line integration
An assembly line is a manufacturing process where partially assembled products move through a series of workstations in a specific order. Components or tasks are added at each station, gradually forming the final product. In contemporary manufacturing, AI-automated assembly lines are prevalent, with machines carrying out most of the tasks and requiring minimal human intervention. This automation significantly improves efficiency, consistency, and productivity in the manufacturing process, reducing errors and enhancing overall output.
Predictive analytics
AI algorithms can predict equipment failures or malfunctions by analyzing sensor data and historical maintenance records. By identifying patterns and trends, manufacturers can proactively schedule maintenance activities, order spare parts in advance, and avoid costly unplanned downtime. This ensures smooth operations, minimizes disruptions, and maximizes the lifespan of machinery, ultimately improving overall equipment effectiveness. Predictive analytics allows manufacturers to optimize maintenance schedules, reduce maintenance costs, and increase production uptime, improving productivity and operational efficiency.
Real-time monitoring and analysis
AI technology enables real-time monitoring of production lines, collecting data from sensors, machines, and other sources. This data is then examined to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and improve overall efficiency. AI algorithms can quickly detect anomalies or deviations from expected performance, enabling manufacturers to take immediate corrective actions. Real-time monitoring and analysis provide valuable insights into production performance, helping manufacturers make data-driven decisions and continuously improve their operations.
Process optimization
AI techniques like machine learning analyze production data to identify inefficiencies and optimize manufacturing processes. AI algorithms can suggest process improvements by analyzing factors such as product cycle times, energy consumption, and material usage. This leads to increased productivity, reduced costs, improved resource utilization, and enhanced overall operational efficiency. Manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, eliminate waste, and implement continuous improvement initiatives to drive productivity gains and achieve higher levels of efficiency.
Energy management
AI algorithms optimize energy usage in manufacturing facilities by analyzing real-time data and identifying patterns of energy wastage. By suggesting energy-saving strategies and optimizing equipment operation, manufacturers can reduce energy costs, enhance sustainability efforts, and meet environmental regulations. This reduces operational expenses and contributes to a greener and more sustainable manufacturing process. Manufacturers can identify energy-intensive processes, implement energy-efficient technologies, and monitor energy consumption to achieve cost savings and environmental benefits.
Supply chain optimization
AI-driven analytics optimize supply chain operations by analyzing various data sources, such as demand forecasts, production capacities, and inventory levels. Manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to streamline procurement, inventory management, and distribution processes. By optimizing these aspects, manufacturers can achieve cost savings, minimize stockouts, improve delivery times, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency. This enables manufacturers to respond quickly to market demands, reduce inventory holding costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
Demand forecasting
AI-powered demand forecasting models utilize historical sales data, new market trends, and external factors to predict future demand accurately. Manufacturers can use these forecasts to align production and inventory levels with anticipated demand. This minimizes stockouts, reduces excess inventory, and improves supply chain responsiveness and customer satisfaction. Accurate demand forecasting allows manufacturers to optimize production schedules, prevent overproduction or stock shortages, and improve overall supply chain agility.
Warehouse management
AI offers multifaceted automation opportunities in warehouse management. With a constant flow of data, manufacturers can enhance inventory oversight and optimize logistics. This automation reduces warehouse management costs, boosts productivity, and diminishes the need for manual quality control and inventory checks, ultimately leading to increased revenue and profitability for manufacturers.
Fair compensation management
Manufacturing facilities commonly provide bonus rewards for employees who put in extra work hours. Yet, accurately evaluating and ensuring equitable compensation for overtime can be a cumbersome task, typically overseen by HR teams in manufacturing companies. The adoption of HR technology, particularly AI-driven solutions, can significantly assist HR professionals in this regard. AI can automate the tracking and management of overtime data, precisely calculating hours worked and bonus entitlements, streamlining the process and minimizing errors while ensuring equitable compensation for employees’ extra contributions.
Reporting
Effective manufacturing relies on data tracking, reporting, and equipment efficiency. HR teams ensure workforce adherence to safety guidelines, necessitating regular compliance reporting. AI assists by automating data analysis for proactive equipment maintenance, streamlining report generation, and using predictive analytics to anticipate safety issues. This integration of AI enhances operational efficiency and safety in manufacturing.
Personalization
Personalization in marketing for AI in manufacturing refers to the practice of personalized marketing efforts and communication to individual customers or target audiences in the manufacturing sector using artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. This approach leverages data-driven insights and predictive analytics to deliver highly relevant and customized marketing messages, products, and services to each recipient.
Email marketing
Email marketing for AI in manufacturing involves sending targeted emails to potential clients and partners in the manufacturing industry. These emails contain valuable content, such as case studies and whitepapers, highlighting the benefits of AI solutions. The audience is segmented based on industry, job roles, and previous interactions, allowing for personalized messaging. Automation tools are used to schedule and track email performance, while lead nurturing efforts aim to convert prospects into customers or partners. Email marketing is vital for building relationships, establishing credibility, and promoting AI solutions in manufacturing.
Copywriting
Copywriting in marketing for AI in manufacturing involves the art of crafting persuasive and engaging written content that effectively communicates the value and products manufactured. It focuses on creating compelling messages, including website copy, product descriptions, email campaigns, and social media posts tailored to resonate with the target audience. The goal is to highlight AI technologies’ efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and transformative potential, ultimately driving leads, conversions, and brand recognition in the manufacturing industry.
Yield optimization and batch analysis
AI for yield optimization and batch analysis plays a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and product quality across various industries, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food processing, and electronics. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and data analytics, AI systems analyze historical production data, environmental conditions, and quality control measurements to identify patterns and factors that influence the manufacturing yield and quality of each batch. This deep analysis enables manufacturers to predict and mitigate issues that could lead to reduced yield or batch failure, optimize production processes for maximum efficiency, and ensure consistent product quality.
Moreover, AI-driven models can dynamically adjust production parameters in real-time based on the analysis of ongoing batch data, further optimizing yields and reducing waste. For instance, in the pharmaceutical industry, AI can predict optimal conditions for drug formulation processes, reducing the risk of batch failure due to instability or contamination. In electronics manufacturing, AI can improve the yield of semiconductor fabrication by identifying and correcting process deviations quickly. This approach in manufacturing management boosts the bottom line by maximizing output, minimizing waste, and ensuring products meet quality standards, enhancing customer satisfaction and competitive advantage.
Smart energy management
Integrating AI-driven smart lighting and HVAC control systems into energy management demonstrates the synergy between artificial intelligence and manufacturing facilities, greatly improving energy efficiency. These AI systems intelligently analyze data on usage patterns, and occupancy levels to automatically adjust lighting and climate control settings in real-time. By doing so, they ensure that energy consumption is optimized, reducing wastage and lowering operational costs. This not only contributes to a substantial reduction in the environmental footprint of manufacturing operations but also aligns with sustainability goals and regulatory compliance. Furthermore, implementing such systems can lead to a more comfortable and productive working environment, indirectly boosting worker satisfaction and overall productivity. The key advantage lies in AI’s ability to learn and predict optimal settings for various conditions, ensuring energy is used judiciously without compromising facility operations or comfort.
Order management
AI-driven order management is a significant use case in manufacturing that greatly streamlines the entire order-to-delivery cycle. By integrating AI, manufacturers can automate and optimize the processing of orders, from initial receipt to fulfillment and shipping. This involves the use of sophisticated algorithms to analyze order data in real-time, predict demand trends, and efficiently allocate resources. For example, AI can prioritize orders based on delivery deadlines, stock availability, and customer importance, ensuring that the most critical orders are fulfilled first. Moreover, AI can identify patterns and insights from historical order data, enabling manufacturers to anticipate future demand spikes or declines and adjust their production schedules and inventory levels accordingly. This proactive approach to order management enhances operational efficiency and improves customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate order fulfillment, reducing lead times, and minimizing stockouts or overproduction.
Additive manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, often known as 3D printing, refers to the process of creating three-dimensional objects by adding material layer by layer based on a digital design. This method involves constructing an item by sequentially laying down thin layers of material until the entire object is built. AI’s integration into 3D printing and additive manufacturing is transforming the field, making significant strides in how objects are designed, produced, and optimized. Using machine learning algorithms, AI enhances the precision and efficiency of 3D printing processes, enabling the creation of complex designs that were previously impossible or too costly to achieve. This advancement in design capabilities allows for more efficient use of materials and reduces waste, leading to more sustainable manufacturing practices. Additionally, AI facilitates the automation of 3D printing operations, enabling machines to self-adjust and make decisions in real-time for optimal performance. This autonomy extends to predictive maintenance, where AI algorithms predict and prevent potential equipment failures, ensuring continuous and efficient production. As a result, manufacturers can produce high-quality, customized products faster and more economically than ever before, opening new possibilities for innovation in various industries, including aerospace, healthcare, and automotive.
Reading text and barcodes with OCR
When enhanced with AI, optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology transforms how businesses handle data by automating the reading and interpretation of texts, images, stamps, and barcodes. This innovation is pivotal in streamlining inventory management systems, allowing for the rapid and accurate digitalization of physical data without the need for manual input. The accuracy of AI-powered OCR drastically reduces the errors typically associated with human data entry, enhancing operational efficiency and reliability. By recognizing and converting various forms of text and barcodes into digital data, organizations can effortlessly track products, manage stocks, and process documents, leading to significant time and cost savings. This technology is particularly beneficial in logistics and retail, where managing vast inventories is crucial for smooth operation. AI’s continuous learning capability further refines OCR’s accuracy, enabling it to adapt to new fonts, handwriting styles, and formats, thus broadening its applicability and effectiveness in diverse settings.
Digital twin simulations
Digital twin simulations represent an innovative use of AI in manufacturing, creating an accurate virtual model of physical manufacturing assets and processes. This technology allows manufacturers to simulate, analyze, and optimize their operations in a virtual space, offering insights that can significantly improve efficiency, productivity, and innovation. The digital twin acts as a dynamic mirror of the real-world manufacturing environment, incorporating data from various sources to predict how processes will perform under different conditions. This capability is particularly valuable for predictive maintenance, where AI algorithms analyze the digital twin to predict potential failures or issues before they occur in the physical world. As a result, manufacturers can preemptively address problems, significantly reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Moreover, digital twin simulations enable the testing of changes to manufacturing processes or the introduction of new products without the need to halt production, thereby minimizing risk and encouraging experimentation and innovation.
Wearable technologies for workplace safety
Integrating AI with wearable technologies such as smart glasses redefines workplace safety in manufacturing and other high-risk environments. These advanced devices can provide workers with hands-free access to vital instructions and information, minimizing distractions and enabling them to focus on the task at hand with enhanced situational awareness. For instance, smart glasses can overlay real-time data, safety alerts, or assembly instructions directly into the wearer’s field of vision. This not only speeds up the completion of tasks but also significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents by ensuring that safety protocols are followed more closely. Furthermore, these wearables can monitor the wearer’s health signs or environmental conditions, alerting them to potential hazards like toxic gas exposure or extreme temperatures. AI plays a crucial role in analyzing the data collected by these devices, offering personalized warnings and recommendations to each worker based on their specific situation and surroundings. This tailored approach to safety, powered by AI and wearable technology, marks a significant leap forward in protecting workers’ well-being while maintaining high productivity levels.
Production scheduling and management
AI-driven production scheduling and management transform the way manufacturing operations are planned and executed. By leveraging AI, these systems can analyze vast amounts of data regarding order backlogs, machine availability, material supply, and workforce capacity to create highly efficient production schedules. The AI algorithms consider various constraints and objectives, such as minimizing downtime, reducing production costs, and meeting delivery deadlines, to optimize the allocation of resources. This not only ensures that production runs smoothly and efficiently but also allows for the dynamic adjustment of plans in response to unforeseen changes or delays. The result is a more agile and responsive manufacturing process that can adapt to the market’s demands while maintaining high productivity levels and minimizing waste. This strategic application of AI in production scheduling and management enables manufacturers to improve operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness significantly.
Managing purchasing price variance
AI for managing purchasing price variance in manufacturing is a strategic application that significantly enhances procurement efficiency and cost management. This use case leverages artificial intelligence to scrutinize and predict fluctuations in raw material costs, which directly impact manufacturing margins. By analyzing detailed attributes of resources—such as pitch, diameter, material type, and finishing—and incorporating supplier-specific data, including country, brand, and performance, AI algorithms can precisely group necessary product parts and forecast standard purchase prices. This forecasting takes into account historical purchase data and prevailing market trends, establishing a benchmark for comparing prices across different suppliers. Consequently, manufacturers gain the advantage of a centralized procurement data management system, streamlining the oversight of parts acquired from various vendors. This AI-driven approach not only optimizes purchasing decisions but also guards against unexpected cost variances, thereby safeguarding and potentially improving profit margins.
Cybersecurity
AI plays a crucial role in enhancing cybersecurity measures in the manufacturing sector. As manufacturers increasingly adopt digital technologies and connect their operations to the internet, they become more vulnerable to cyber threats that can disrupt production lines, steal sensitive data, and compromise the safety of automated systems. AI-driven cybersecurity solutions can proactively detect and respond to these threats in real-time. This is achieved by continuously monitoring network activity for unusual patterns or anomalies that may indicate a security breach. Using machine learning algorithms, AI systems can learn from past incidents and adapt to new and evolving threats, making them more efficient over time. Furthermore, AI can automate the response to detected threats, isolating affected systems and preventing the spread of malware or the execution of cyberattacks. This proactive and adaptive approach not only secures the manufacturing process against disruptions but also protects intellectual property and sensitive customer data, maintaining trust and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Streamlining manufacturing processes with generative AI
Generative AI is transforming the manufacturing industry by streamlining various stages of production, from concept and design to distribution and maintenance. By leveraging advanced algorithms, GenAI enhances decision-making, automates routine tasks, and drives continuous improvement throughout the entire manufacturing lifecycle. Below is an overview of how GenAI plays a role at each step of the manufacturing process, optimizing operations and boosting efficiency.
1. Concept and design
| Steps | Sub-Steps | Role of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Initiate Idea |
|
|
| Design Prototype |
|
|
| Raw Material Procurement |
|
|
| Prototype Testing |
|
|
| Finalize Concept |
|
|
2. Planning and scheduling
| Steps | Sub-Steps | Role of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Allocation |
|
|
| Timeline Creation |
|
|
| Production Goal Setting |
|
|
3. Procurement and inventory
| Steps | Sub-Steps | Role of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Material Sourcing |
|
|
| Inventory Management |
|
|
| Supplier Coordination |
|
|
4. Production and quality control
| Steps | Sub-Steps Involved | Role of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Production Execution |
|
|
| Real-Time Monitoring |
|
|
| Quality Control |
|
|
5. Distribution and maintenance
| Steps | Sub-Steps Involved | Role of Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Packaging and Labeling |
|
|
| Distribution Coordination |
|
|
| Maintenance and Continuous Improvement |
|
|
Incorporating generative AI into manufacturing processes offers a transformative approach to improving efficiency, reducing costs, and driving innovation. By automating key tasks, providing real-time insights, and ensuring continuous optimization, genAI empowers manufacturers to stay competitive in an increasingly complex market.
How LeewayHertz’s advanced generative AI platform optimizes manufacturing processes
LeewayHertz’s generative AI platform, ZBrain, stands as a pivotal solution for manufacturing enterprises aiming to confront challenges within their workflows, enhancing efficiency and fostering business growth. ZBrain enables enterprises to develop tailored LLM-based applications, optimizing workflows, improving customer interactions, and advancing manufacturing operations. The platform uses clients’ data, whether in the form of text, images, or documents, to train advanced LLMs like GPT-4, Vicuna, Llama 2, or GPT-NeoX for developing contextually aware applications capable of performing diverse tasks. These applications contribute to informed decision-making, provide in-depth insights, and enhance productivity, all while maintaining stringent data privacy standards.
In the manufacturing sector, challenges such as suboptimal forecasting accuracy, resource allocation inefficiencies, and prolonged decision-making processes are prevalent. ZBrain effectively addresses these challenges through its specialized Flow feature, which provides an intuitive interface where users can create intricate business logic for their apps without the need for coding. Flow’s easy-to-use drag-and-drop interface enables the seamless integration of large language models, prompt templates, and media models into your app’s logic for its easy conceptualization, creation, or modification.
Sophisticated apps created using Flow play a transformative role in converting intricate manufacturing data into actionable insights. This offers holistic solutions to some of the most pressing challenges encountered in manufacturing workflows, resulting in heightened efficiency, minimized error rates, and elevated overall production quality. Here are some examples –
AI-driven supply chain optimization
ZBrain effectively addresses complex supply chain optimization challenges in manufacturing. With LLM-based applications developed with clients’ business data, ZBrain enhances supply chain transparency, accurately forecasts demand, and improves inventory management. This results in numerous benefits, including reduced operational costs, minimized waste, and faster delivery times. To understand how ZBrain’s methodology promotes a more responsive and efficient supply chain adept at quickly adapting to market changes and customer needs, you can check out this page.
AI-driven quality control and defect analysis
ZBrain significantly enhances quality control and defect analysis in the manufacturing sector. The LLM-based applications developed using ZBrain efficiently pinpoint product defects, ensuring higher accuracy and consistency in quality assessments. This innovation reduces the time and resources traditionally required for manual inspections, thereby elevating product quality and enhancing operational efficiency. For a detailed understanding of how ZBrain transforms manufacturing processes with more precise, dependable, and cost-effective solutions and how it supports businesses in maintaining superior quality standards, you can check out the specific quality control Flow here.
AI-driven production planning and optimization
ZBrain apps significantly improve production planning and optimization in manufacturing. They enable firms to accurately forecast, effectively allocate resources, and streamline production schedules. This leads to enhanced efficiency, reduced waste, and better use of resources. Implementing ZBrain apps allows manufacturers to quickly adapt to market changes and boost productivity, elevating their production management strategies. To understand the detailed process and see the impact of ZBrain on production planning, you can explore the comprehensive Flow process here.
AI-driven automated supplier evaluation
ZBrain effectively transforms the process of supplier evaluation in manufacturing. With powerful LLM-powered applications, it automates the assessment of supplier performance and compliance, thereby boosting supply chain efficiency. This results in quicker, more precise evaluations, minimizes supply chain disruption risks and aids in making better decisions. This innovation leads to a more reliable supplier network, contributing to smoother production processes and enhanced overall business performance. To gain a comprehensive view of how ZBrain refines supplier evaluation, you can refer to the detailed Flow provided here.
AI-driven patent management optimization
ZBrain redefines patent management for manufacturing enterprises, addressing challenges related to complex portfolios, time-consuming analysis, legal intricacies, and strategic decision-making. In the competitive manufacturing landscape, safeguarding intellectual property is crucial, and ZBrain’s AI-driven apps streamline the patent management process. The initial phase involves automated data collection, where ZBrain gathers pertinent information such as existing patents, prior art references, legal compliance records, and industry trends. Subsequently, an automated Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) is conducted to extract meaningful insights. This EDA includes a comprehensive examination of the patent landscape, identifying key features and potential infringements that could impact patent management. ZBrain’s innovative approach significantly impacts patent management in the manufacturing industry, offering a simplified and efficient process. Explore this Flow to understand how ZBrain enhances patent management, providing manufacturing excellence through streamlined processes and improved intellectual property protection.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
LeewayHertz’s AI development services for manufacturing
At LeewayHertz, we design tailored AI solutions that cater to the unique needs of manufacturing firms. Our strategic AI/ML consulting enables manufacturers to leverage AI for enhanced production efficiency, improved quality control, and optimized supply chain management.
Our expertise in developing Proof of Concepts (PoCs) and Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) allows manufacturing firms to assess the potential impacts of AI tools in real-world scenarios, ensuring that the solutions are both effective and tailored to the specific requirements of the manufacturing sector.
Our work in generative AI also transforms routine tasks such as predictive maintenance and production planning, automating these processes to free up engineers for more strategic roles.
By fine-tuning large language models to the nuances of manufacturing terminology and processes, LeewayHertz enhances the accuracy and relevance of AI-driven communications and analyses.
Additionally, we ensure seamless integration of AI systems with existing technological infrastructures, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making in manufacturing firms.
Our AI solutions development expertise
AI solutions development for manufacturing typically involves creating systems that enhance production efficiency, automate routine tasks, and improve product quality. These solutions integrate key components such as data aggregation technologies, which compile and analyze production data from diverse sources. This comprehensive data foundation supports predictive analytics capabilities, allowing for the forecasting of equipment failures and production bottlenecks that inform strategic decisions. Additionally, machine learning algorithms are employed to optimize production schedules and supply chain logistics, ensuring that each step in the manufacturing process is as efficient as possible. These solutions often cover areas like predictive maintenance, quality control, supply chain optimization, and production planning.
Overall, AI solutions in manufacturing aim to optimize production outcomes, improve efficiency, and elevate product quality.
AI agent/copilot development for manufacturing
LeewayHertz builds custom AI agents and copilots that enhance various manufacturing operations, enabling companies to save time and resources while facilitating faster decision-making. Here is how they help:
Predictive maintenance:
- Monitoring equipment health using historical maintenance data, equipment specifications, sensor readings, and production records to identify patterns indicating potential failures.
- Scheduling maintenance activities proactively to prevent unplanned downtime.
- Generating detailed reports on equipment performance and maintenance needs.
Quality control:
- Analyzing production data to identify defects and quality issues in real-time.
- Providing recommendations for process adjustments to maintain high-quality standards.
Supply chain optimization:
- Predicting demand and optimizing inventory levels based on historical data and market trends.
- Automating the procurement process to ensure timely availability of raw materials.
- Enhancing logistics by optimizing delivery routes and schedules.
Production planning:
- Gathering and analyzing data from diverse sources, providing manufacturers with a comprehensive view of their production processes.
- Customizing production schedules based on real-time data, ensuring optimal resource utilization.
- Providing manufacturers with real-time insights into production bottlenecks and inefficiencies, supporting timely and informed decision-making.
Process automation:
- Automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and report generation.
- Automating data validation and verification tasks.
- Automating the management of production workflows and resource allocation.
Defect detection:
- Monitoring production lines for predefined patterns or rules associated with defects.
- Flagging potential quality issues based on predefined criteria or models.
Customer segmentation and targeting:
- Analyzing customer data to segment them based on predefined criteria (e.g., purchasing behavior, product preferences).
- Identifying potential cross-selling or upselling opportunities based on customer segments.
AI agents/copilots don’t just increase the efficiency of operational processes but also significantly enhance the quality of product development and strategic decision-making. By integrating these advanced AI solutions into their existing infrastructure, manufacturing firms can achieve a significant competitive advantage, navigating the complex industrial landscape with innovative, efficient, and reliable AI-driven tools and strategies.
How does AI address key challenges across every step of the manufacturing workflow?
The manufacturing workflow can vary significantly depending on the industry type and the specific product being manufactured. Manufacturers face various challenges throughout the different steps of the manufacturing workflow, and AI can help address some of these challenges. Here are key challenges and ways AI can contribute:
Product design and development:
Challenge: Design iterations and optimization can be time-consuming.
AI solution: Generative design algorithms can quickly explore multiple design options based on specified criteria, helping designers identify optimal solutions faster.
Materials procurement:
Challenge: Fluctuating raw material costs and supply chain disruptions.
AI solution: Predictive analytics and ML algorithms have the capability to analyze historical data and market trends to forecast material costs and identify potential supply chain disruptions, enabling proactive decision-making.
Quality control:
Challenge: Detecting defects or anomalies in real time.
AI solution: Computer vision systems powered by AI can inspect and identify defects on the production line, reducing the reliance on manual inspection and improving accuracy.
Production planning:
Challenge: Dynamic demand fluctuations and resource allocation complexities.
AI solution: AI-based demand forecasting and production planning tools can analyze historical data, market trends, and other factors to optimize production schedules and resource allocation in real time.
Engineering and manufacturing:
Challenge: Maintaining optimal production efficiency and quality.
AI solution: AI-driven process optimization and control systems can adapt manufacturing processes in real time, ensuring efficiency and quality while minimizing waste.
Quality assurance:
Challenge: Identifying and addressing defects quickly.
AI solution: Machine learning models can learn from historical defect data to predict and prevent defects in real time, improving overall product quality and reducing rework.
Warehousing and distribution:
Challenge: Efficient inventory management and logistics planning.
AI solution: AI-powered inventory management systems can optimize stock levels, predict demand, and enhance logistics planning, reducing costs and minimizing stockouts or overstock situations.
Sales and marketing:
Challenge: Targeting the right audience and optimizing marketing strategies.
AI solution: AI-driven analytics can analyze customer behavior, preferences, and market trends to personalize marketing strategies, improving customer targeting and increasing sales effectiveness.
Customer service:
Challenge: Handling customer inquiries and issues efficiently.
AI solution: AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine inquiries, providing quick responses and freeing up human agents to address more intricate and challenging issues.
Maintenance and upkeep:
Challenge: Downtime due to unexpected equipment failures.
AI solution: Predictive maintenance models can analyze equipment sensor data to predict potential failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing unplanned downtime.
Continuous improvement:
Challenge: Identifying areas for improvement and innovation.
AI solution: AI analytics can analyze operational data to identify inefficiencies and recommend improvements, contributing to continuous process optimization.
AI technologies can enhance various aspects of the manufacturing process, providing manufacturers with data-driven insights, predictive capabilities, and automation tools to overcome challenges and optimize efficiency.
How can AI be implemented in the manufacturing workflow for enhanced efficiency and innovation?
Implementing AI in manufacturing workflow involves a strategic and step-by-step approach. Here’s a general guide on how to go about it:
Define objectives: Clearly define the goals you aim to achieve by implementing AI in the manufacturing process. Whether it’s improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing quality, or all of the above, having a clear vision will guide your implementation strategy.
Monitor current processes: Conduct a thorough assessment of your existing manufacturing processes. Identify bottlenecks, areas for improvement, and tasks that can be automated or optimized using AI.
Data collection and integration: AI relies heavily on data. Ensure that you have access to relevant and high-quality data. This may involve integrating various data sources within your organization, such as production data, quality control data, and supply chain data.
Infrastructure and technology: Allocate resources to acquire the essential infrastructure and technologies required for the successful implementation of AI. This may include cloud computing resources, powerful hardware, and AI software platforms.
AI skillset: Build or hire the necessary expertise. If your team lacks AI skills, consider training your existing workforce or hiring professionals with AI expertise. Alternatively, collaborate with AI service providers or consultants.
Pilot projects: Commence with pilot projects to test the feasibility and effectiveness of AI applications in specific areas of your manufacturing workflow. This allows you to evaluate the impact on a smaller scale before full-scale implementation.
Select appropriate AI technologies: Choose the right AI technologies based on your objectives and the nature of your manufacturing processes. This may include machine learning algorithms, computer vision, natural language processing, and predictive analytics.
Integration with existing systems: Ensure seamless integration with your existing systems and technologies. This might involve collaboration with your IT department to connect AI solutions with ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, MES (Manufacturing Execution System), and other relevant platforms.
Employee training and change management: Prepare your workforce for the changes introduced by AI. Provide training programs to familiarize employees with the new technologies and processes. Emphasize the advantages and address any concerns they may have.
Scale implementation: Once the pilot projects prove successful and the workforce is adequately trained, scale up the implementation of AI across the entire manufacturing workflow. Monitor the performance and continually refine the systems based on feedback and data analysis.
Continuous monitoring and improvement: Implement a system for continuous monitoring of AI applications. Regularly assess their performance, identify areas for improvement, and update algorithms or processes accordingly.
Cybersecurity measures: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard sensitive data and AI systems from potential threats. This is crucial to ensure the integrity and security of your manufacturing operations.
Compliance and regulations: Stay informed about industry regulations and compliance standards related to AI in manufacturing. Ensure that your AI implementations align with legal and ethical guidelines.
If you’re seeking a technological partner to advance your manufacturing capabilities, LeewayHertz stands as your reliable ally. Specializing in AI consulting and development services, LeewayHertz is dedicated to boosting your manufacturing operations into the digital forefront. With a demonstrated track record in implementing a variety of advanced AI models and solutions, LeewayHertz is poised to assist you in initiating or advancing your AI journey within the manufacturing sector.
Ethical considerations in the deployment of AI within the manufacturing sector
Implementing AI in manufacturing brings with it a range of ethical considerations that organizations need to navigate carefully to ensure responsible deployment. Key ethical considerations include:
- Bias and fairness: AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate biases present in their training data, leading to discriminatory outcomes. Ensuring fairness requires thorough investigation and mitigation of these biases to prevent AI from misinterpreting data and proliferating errors. This includes implementing fairness-aware algorithms and conducting regular audits to maintain societal principles of fairness.
- Transparency and explainability: The decision-making processes of AI, often referred to as “black-box” algorithms, can be opaque, making it challenging to verify their accuracy and potentially leading to questionable outcomes. Ethical AI demands that these processes be transparent and understandable, allowing for accountability and fostering user confidence.
- Data privacy and security: Handling sensitive manufacturing data necessitates robust measures to protect against unauthorized access and breaches. This includes employing strong cybersecurity measures, such as encryption and access controls, to safeguard proprietary information and intellectual property.
- Accountability: Organizations must accept accountability for both the intended and unintended consequences of AI, understanding that liability risks are a significant aspect of AI deployment. This includes being prepared for negative outcomes that can impact stakeholders across the organization and ensuring that strategies are in place to prevent and address such scenarios.
- Regulatory compliance and ethical oversight: Strengthening existing regulations and incorporating ethical considerations into legal frameworks are essential for responsible AI deployment. Collaborative efforts across industries to establish ethical guidelines and the inclusion of varied expertise in ethical oversight teams can ensure that AI applications align with ethical and societal norms.
Addressing these ethical considerations requires a concerted effort across different departments within an organization, including legal, data science, and risk management, as well as collaboration with external experts. By focusing on these key areas, manufacturers can successfully adopt AI in a manner that is both responsible and beneficial to the business, its employees, and society at large.
AI in manufacturing: Key technologies and techniques
AI technologies utilized in manufacturing include machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, robotics, and data analytics. Here’s a breakdown of all the AI technologies used in the manufacturing industry:
- Machine learning: Machine learning algorithms analyze large datasets to identify patterns and make predictions for production procedures. This enables manufacturers to optimize processes, predict maintenance needs, and improve product quality. For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to identify patterns that indicate machine failure, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Computer vision: Computer vision involves the usage of AI algorithms to analyze visual data from cameras or sensors. In manufacturing, computer vision can be used to detect defects, monitor production lines, and automate quality control processes. For instance, computer vision systems can quickly identify product defects or anomalies, ensuring that only high-quality products reach the market.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables machines to understand and process human language. In manufacturing, NLP can be used to analyze text data from various sources, such as customer feedback, maintenance logs, or sensor readings. This allows manufacturers to gain valuable insights, automate data analysis, and improve decision-making. For example, NLP can analyze customer feedback to identify trends and sentiments, helping manufacturers improve their products and services.
- Robotics: AI-powered robotics, specifically collaborative robots or cobots, work alongside human workers in manufacturing. These robots can perform repetitive or dangerous tasks, increasing productivity and worker safety. Cobots can be programmed using AI techniques to adapt to different manufacturing processes, improving flexibility and efficiency.
- Data analytics: AI techniques enable manufacturers to analyze large volumes of data and obtain valuable insights. Data analytics in manufacturing can optimize production processes, identify bottlenecks, and improve operational efficiency. For instance, data analytics can help manufacturers optimize inventory management, forecast demand accurately, and streamline supply chain operations.
Benefits of AI in manufacturing
AI in the manufacturing industry brings numerous benefits, improving efficiency and productivity, reducing costs and optimizing processes. Here are some benefits of AI in manufacturing:
Improved efficiency and productivity: AI in manufacturing facilitates process automation, data analysis, and optimization. Through automation, mundane and repetitive tasks are efficiently handled, minimizing the risk of human errors and ensuring consistent quality. This boosts productivity and allows for reallocating human resources to more creative and strategic roles. Moreover, AI-driven data analysis provides valuable insights into production trends and performance, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions for continuous improvement. The integration of AI in manufacturing processes significantly enhances operational efficiency and competitiveness in the global market.
Enhanced quality control: AI plays a pivotal role in manufacturing by conducting real-time inspections and swiftly identifying product defects or anomalies. This proactive approach guarantees top-notch products are delivered to the market, minimizing the need for costly rework, reducing scrap material wastage, and mitigating customer complaints. These systems excel in precision and consistency, surpassing human capabilities in detecting even the slightest imperfections or irregularities, enhancing overall product quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency.
Cost reduction: AI-driven analytics serve as a powerful tool for manufacturers to pinpoint inefficiencies in various critical areas such as production processes, supply chains, and inventory management. AI can identify bottlenecks, underutilized resources, or excessive inventory levels through data analysis and pattern recognition, enabling companies to take corrective actions. This optimization significantly reduces costs, minimizes waste, and streamlined operations. Manufacturers can allocate resources more effectively, improve productivity, and enhance their competition in the market, ultimately contributing to increased profitability and sustainability.
Accurate demand forecasting: AI models leverage historical sales data, market trends, seasonality, and external factors to generate highly accurate demand forecasts. These forecasts enable manufacturers to make informed decisions, ensuring that production levels align precisely with market demand. Consequently, companies can optimize inventory management, reduce the likelihood of stockouts, minimize excess inventory holding costs, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency. This proactive approach improves customer satisfaction by consistently meeting demands and reducing operational expenses, resulting in increased profitability.
Improved safety: Collaborative robots, often referred to as cobots, represent a significant advancement in workplace safety. These robots are equipped with AI algorithms that enable them to work seamlessly alongside human employees, taking on repetitive or hazardous tasks. By doing so, cobots not only enhance worker safety but also reduce the potential for accidents in the workplace. This collaborative approach promotes a safer and more efficient working environment where humans and robots complement each other’s strengths, ultimately leading to increased workplace safety and productivity.
Real-time data analysis: AI technologies empower manufacturers with the capability to conduct real-time data analysis, offering valuable insights and decision-making support. These technologies enable continuous monitoring of production processes, supply chain dynamics, and evolving customer preferences. Consequently, manufacturers can swiftly adapt to shifting demands and market conditions, optimize resource allocation, minimize disruptions, and ultimately enhance operational efficiency and competitiveness in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Product innovation: By scrutinizing vast datasets, AI can unlock valuable insights that may have been overlooked manually, allowing manufacturers to pinpoint specific areas for improvement. This data-driven approach empowers them to refine existing products and create innovative solutions that align more closely with customer needs and preferences. Ultimately, AI-driven product design enhances customer satisfaction, fosters competitive advantage, and accelerates the development of cutting-edge offerings in the market.
Enhanced supply chain management: AI-powered analytics play a pivotal role in supply chain optimization by delving into vast datasets encompassing demand fluctuations, inventory levels, logistics routes, and supplier performance metrics. This comprehensive analysis empowers manufacturers to make informed decisions, fine-tune procurement processes, minimize excess inventory carrying costs, and optimize stock levels. Furthermore, AI-driven insights enhance the efficiency of logistics operations, ultimately ensuring that products are delivered punctually, reducing delays and enhancing overall supply chain performance.
Sustainability and energy efficiency: AI algorithms play a pivotal role in optimizing energy consumption in manufacturing by continuously analyzing real-time data from machinery and processes. These algorithms can pinpoint inefficiencies, forecast energy demand, and recommend adjustments, such as optimizing equipment runtime or scheduling energy-intensive tasks during off-peak hours. This proactive approach reduces energy costs and aligns with sustainability objectives, as it helps manufacturers minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to a more environmentally friendly and energy-efficient production ecosystem.
Optimize Your Operations With AI Agents
Optimize your workflows with ZBrain AI agents that automate tasks and empower smarter, data-driven decisions.
Future trends and opportunities
AI in smart factories and Industry 4.0:
The future of manufacturing lies in the integration of AI technologies in smart factories, which are the cornerstone of Industry 4.0. Smart factories leverage AI to create interconnected systems that enable real-time data exchange, automation, and decision-making. In smart factories, AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data collected from sensors, machines, and production systems. This data-driven approach facilitates predictive maintenance, demand forecasting, and optimization of production processes. AI-powered systems can autonomously adjust production parameters, optimize energy consumption, and detect anomalies in real time, leading to increased efficiency and reduced costs.
Collaborative robots (cobots) and human-robot interaction:
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are a growing trend in manufacturing, combining the strengths of AI and robotics to facilitate human-robot collaboration. Unlike traditional industrial robots that operate in isolation, cobots work alongside human workers, enhancing productivity and flexibility. Cobots are equipped with AI algorithms that enable them to perform tasks cooperatively and safely. They can adapt to production environment changes, work close to humans, and learn from human guidance. These cobots can take over repetitive, physically demanding, or hazardous tasks while humans focus on more complex and creative work. The interaction between humans and cobots is facilitated through natural language processing, gesture recognition, and computer vision. This enables intuitive communication and seamless collaboration between humans and machines. Combining AI and cobots offers opportunities for increased productivity, improved ergonomics, and efficient resource utilization in manufacturing processes.
AI-enabled decision support systems for manufacturing executives:
AI-enabled decision support systems empower manufacturing executives with real-time insights, predictive analytics, and scenario modeling to make informed decisions and drive strategic initiatives. These systems utilize AI algorithms to process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and generate actionable recommendations. Manufacturing executives can leverage AI-driven decision support systems for demand forecasting, capacity planning, and supply chain optimization. These systems provide accurate forecasts by analyzing historical data, market trends, and customer preferences, enabling executives to optimize production schedules, resource allocation, and inventory levels. Moreover, AI-enabled decision support systems assist in risk assessment and mitigation strategies. AI algorithms can analyze data from several sources, including supply chain disruptions, market fluctuations, and regulatory changes, to identify potential risks and propose proactive mitigation measures.
Leveraging AI agents for optimizing manufacturing processes for quality and efficiency
An AI agent, essentially a computer program or system, functions autonomously to interpret its surroundings, make decisions, and execute actions aimed at accomplishing specific objectives. These agents are categorized into various types, each defined by distinct characteristics. Reactive agents respond to immediate stimuli, while proactive agents plan ahead. Moreover, agents may operate within fixed or dynamic environments, with the latter demanding adaptability. Multi-agent systems involve multiple agents collaborating towards shared goals, often necessitating coordination and communication. AI agents are widely utilized across diverse domains such as robotics, gaming, and intelligent systems, leveraging a range of programming languages and techniques, including machine learning and natural language processing. Auto-GPT, an intelligent agent, is a popular example of an AI agent that streamlines operations by automating multi-step tasks, effectively linking subtasks to achieve predefined objectives, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
In this context, tools like AutoGen Studio streamline the processes of development and management of multi-agent AI applications, simplifying the development lifecycle. Similarly, CrewAI, another AI agent development framework, facilitates collaborative efforts among AI agents, enabling them to tackle complex tasks through coordinated role-playing and task delegation.
Applications of AI agents in manufacturing
The applications of AI agents in manufacturing are diverse and impactful, contributing to improved efficiency, productivity, and quality for businesses. Here are some key applications:
- Predictive maintenance: AI agents transform maintenance practices by analyzing sensor data from manufacturing equipment. By detecting subtle patterns and anomalies in the sensor data, these agents predict potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach allows for scheduled maintenance, minimizing downtime and reducing maintenance costs significantly. Additionally, AI agents help in prioritizing maintenance tasks based on criticality, ensuring optimal equipment performance and longevity.
- Production optimization: AI agents play a pivotal role in optimizing production schedules and resource allocation. By analyzing vast amounts of production data and demand forecasts, these agents streamline production processes to maximize efficiency and minimize waste. They intelligently schedule machine operations, adjust inventory levels, and optimize workflow sequences to meet customer demand while minimizing costs and maximizing profitability.
- Supply chain management: AI agents redefine supply chain operations by leveraging predictive analytics and optimization algorithms. These agents forecast demand accurately, manage inventory levels efficiently, and optimize logistics routes for timely delivery. By analyzing historical data and external factors, AI agents make data-driven decisions that enhance supply chain efficiency, reduce lead times, and improve overall operational performance.
- Process optimization and control: AI agents optimize manufacturing processes by continuously monitoring and adjusting parameters in real time. By analyzing sensor data and production metrics, these agents identify opportunities for process improvement and implement adjustments to maintain optimal operating conditions. They dynamically optimize parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed, ensuring consistent product quality and maximizing operational efficiency.
- Demand forecasting and planning: AI agents reshape demand forecasting and production planning by analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and external factors. These agents accurately forecast demand for manufactured products, enabling precise production planning and inventory management. By aligning production levels with anticipated demand, AI agents prevent stockouts or overstock situations, thereby reducing inventory carrying costs and maximizing revenue potential.
Overall, AI agents play a critical role in modern manufacturing by enhancing operational efficiency and enabling agile and adaptive production processes.
Transform your manufacturing operations with LeewayHertz’s AI agent development services
If you are seeking to redefine your manufacturing operations with AI agents, engage LeewayHertz’s AI agent development services. We specialize in creating custom AI agents for manufacturing businesses designed to optimize processes, improve quality control, and increase productivity. Benefit from our expert consultation and strategic guidance, customized to integrate AI agents into your existing workflows and systems seamlessly. Our advanced AI agent-based solutions harness state-of-the-art technologies such as machine learning and LLMs to ensure adaptive and efficient manufacturing operations. Partner with LeewayHertz to unlock the full potential of AI agents and ensure your manufacturing operations are optimized for efficiency.
Conclusion
The diverse applications of AI in manufacturing span quality control, defect detection, predictive maintenance, and product design. AI’s advantages to manufacturing enterprises and examined forthcoming industry trends. The discourse clearly illustrates that AI presents a range of opportunities for manufacturers, allowing them to streamline processes, potentially cut costs, make informed data-centric decisions, and stimulate innovation. By integrating AI technologies, manufacturers can strive to secure a competitive edge, enhance their responsiveness to customer needs, and stay abreast of the ever-evolving digital landscape. To effectively tap into AI’s potential, manufacturers may contemplate investments in research and development, facilitating workforce upskilling and exploring strategic partnerships with AI technology providers, thereby driving ongoing progress and innovation.
Leverage the potential of AI to drive efficiency, enhance quality, and optimize processes in your manufacturing business. Contact LeewayHertz now for your AI consultancy and development needs.
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.
FAQs
How can AI benefit the manufacturing industry?
AI brings several advantages to the manufacturing industry, including improved efficiency through automation, predictive maintenance to reduce downtime, enhanced product quality through defect detection, and optimized supply chain management for better resource utilization.
What specific challenges in manufacturing can AI address?
AI addresses challenges such as production inefficiencies, quality control issues, equipment breakdowns, and supply chain disruptions. Through predictive analytics and other ML techniques, AI can offer immediate insights to address these challenges and enhance the optimization of manufacturing processes.
How does AI improve predictive maintenance in manufacturing?
AI enhances predictive maintenance by analyzing historical and real-time data from machinery. It predicts potential equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance, minimizing downtime, and optimizing the lifespan of critical manufacturing assets.
Can AI be integrated with existing manufacturing systems, or does it require a complete overhaul?
AI integration is flexible and can be implemented incrementally. LeewayHertz specializes in seamless AI integration, ensuring that the AI solutions you incorporate complement your existing manufacturing systems. This approach minimizes disruptions and allows for a gradual transition to AI-driven processes.
How can AI be used to assist in manufacturing systems?
AI plays a significant role in enhancing manufacturing systems by offering innovative solutions that optimize processes and improve overall efficiency. Through machine learning algorithms, AI can analyze vast datasets to predict equipment maintenance needs, reducing downtime and preventing unexpected failures. Additionally, AI-driven automation streamlines production lines, enhancing precision and reducing errors. Collaborative robots powered by AI contribute to tasks like assembly and quality control. Overall, AI transforms manufacturing by introducing predictive maintenance, automation, and intelligent decision-making, leading to increased productivity and cost-effectiveness in manufacturing systems.
Can LeewayHertz provide AI solutions for predictive maintenance to minimize downtime in our manufacturing facility?
Absolutely. LeewayHertz excels in implementing AI solutions for predictive maintenance in manufacturing. Our applications analyze machine data to predict potential breakdowns, enabling proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime, thus optimizing your manufacturing operations.
What security measures does LeewayHertz implement to safeguard sensitive data in AI-driven manufacturing systems?
LeewayHertz prioritizes data security by implementing robust encryption, access controls, and compliance with industry standards. Our AI-driven manufacturing systems are designed to protect sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality and integrity throughout the manufacturing processes.
Can LeewayHertz build customized AI applications for my manufacturing business to address specific operational challenges?
Certainly, LeewayHertz excels in tailoring AI applications to address your manufacturing enterprise’s specific requirements. Our tailored solutions focus on addressing specific operational challenges, ensuring maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
What kind of support does LeewayHertz offer after AI implementation?
LeewayHertz provides comprehensive post-implementation support for AI solutions in manufacturing. This includes regular system maintenance, troubleshooting, and updates to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, their support team is available for any issues or queries that may arise, ensuring seamless integration and continuous improvement of the AI solutions implemented in the manufacturing processes.
Can LeewayHertz assist my small or medium-sized manufacturing enterprise in adopting AI, or is it more suitable for larger enterprises?
LeewayHertz caters to businesses of all sizes. Our AI solutions demonstrate flexibility, easily customized to align with the distinct needs of small and medium-sized manufacturing enterprises. This provides these businesses with cost-effective alternatives for enhancing efficiency and automating processes.
- What is AI in manufacturing?
- AI in manufacturing: Use cases across various departments
- AI use cases in manufacturing
- How LeewayHertz's advanced generative AI platform optimizes manufacturing processes
- LeewayHertz’s AI development services for manufacturing
- How does AI address key challenges across every step of the manufacturing workflow?
- How can AI be implemented in the manufacturing workflow for enhanced efficiency and innovation?
- Ethical considerations in the deployment of AI within the manufacturing sector
- AI in manufacturing: Key technologies and techniques
- Benefits of AI in manufacturing
- Leveraging AI agents for optimizing manufacturing processes for quality and efficiency
- Future trends and opportunities
- Contact us




















