Your app design must offer a great user experience.
Your app should offer a simple yet visually appealing design to attract users attention.
It should be immediately familiar because you generally follow the design precedents and standards offered by other apps. When first looking at your app, a user should think “I know how to use this” without immediately seeking a user guide.
The task of making an app simple is anything but simple. UX (User Experience) designers can spend days or even months working out the layout, the controls and other user interface elements to deliver the best user experience. When it come to designing the interface to control a camera, they often don’t commit the same time and resources. Instead, they simply integrate the basic camera control with a button to take photos and videos. While convenient for the designer, this approach may lead to a user experience that is less than ideal.
There are numerous design issues to be considered when implementing a camera controller. UX designers should design apps that factor in these issues to offer the best user experience.
A significant challenge faced by UX designers working on camera controllers is the variation of photo content. The camera can be pointed at anything so the background of the user interface can be light or dark, simple or complex. It could be a sunny beach, a snowy mountain or a crowded rock concert. The more complex the view, the more difficult it becomes to give the user the same experience as the designer planned in the design lab.
How do UX designers design apps which meet this challenge and offer great camera controller user interfaces?
Let’s look at the top five photo and video apps available in the App Store to see how they address the problem. Next we’ll make recommendations to help you design apps with an outstanding user experience.
iPhone Native Camera App
Apple’s native iPhone Camera app comes free with the iOS operating system and is used by hundreds of millions of users. It saves full screen photos into the photos app, but while taking photos the photo image occupies only about 70% of the screen. The view is confined to a square or rectangular window. Big black bars are added to the top and bottom of the screen to make the camera controls easy to see regardless of the image viewed in the camera. While recording video, the bars become semi-opaque. The camera buttons are color coded for taking photos and videos. Users can pinch and zoom before taking photos, but not with the front camera.
The Camera app does not offer a preview after the photo is taken, it simply saves the photo into the native Photos app. If you want to adjust the photo or add effects you must take the photo first, then apply the filters. The speed of taking photos is so fast it can be difficult to determine whether the photo has been saved. Photos taken with the front camera are auto-flipped to eliminate mirroring problems. If not for this feature, the text on your t-shirt would appear backward in your selfie. When photos are shared across different apps (e.g. WhatsApp) they do not appear in full screen.
Facebook App Front Camera
Facebook App Rear Camera View
The Facebook iPhone app and Messenger app offer a full screen camera for taking pictures and recording video. The camera controls are placed at the bottom of the screen with a white icon neatly placed on a black overlay so they are visible regardless of the camera view. Facebook makes use of gestures in the interface. A single tap focuses the camera on any object and double tapping flips between the front and back camera. Tapping and holding the shutter button switches between taking a photo and recording a video. Gestures can be very convenient for the user and should not be overlooked when you design apps.
Facebook has invested in improving its camera features and they have come a long way from the single-pixel based camera controls that they had in previous versions. You can now add effects to the live camera view before taking the photo. Despite this, the Facebook camera user experience has a few shortcomings. When using selfie mode, the photo has to be flipped manually to avoid mirroring.
Instagram App Camera
Instagram is a popular photo sharing site. The Instagram iOS app ensures the photo you take will be exactly the same when it appears on your friend’s wall after you share it. To achieve this, the Instagram app only allows square photos. This results in the camera controller using only 60% of the screen space to display the image.
The Instagram app is a simple interface that is easy to use.
Most controls are text labels on a white background that are easily seen and that are easy to understand. They are simpler for novices than icons that have to be interpreted, but when you design apps using this type of interface you may have to translate the text into other languages if your app goes global. Two icons remain in the Instagram user interface: the flash control and the front/back camera switch. These are placed over the photo image and are far less obvious than the controls over the white background.
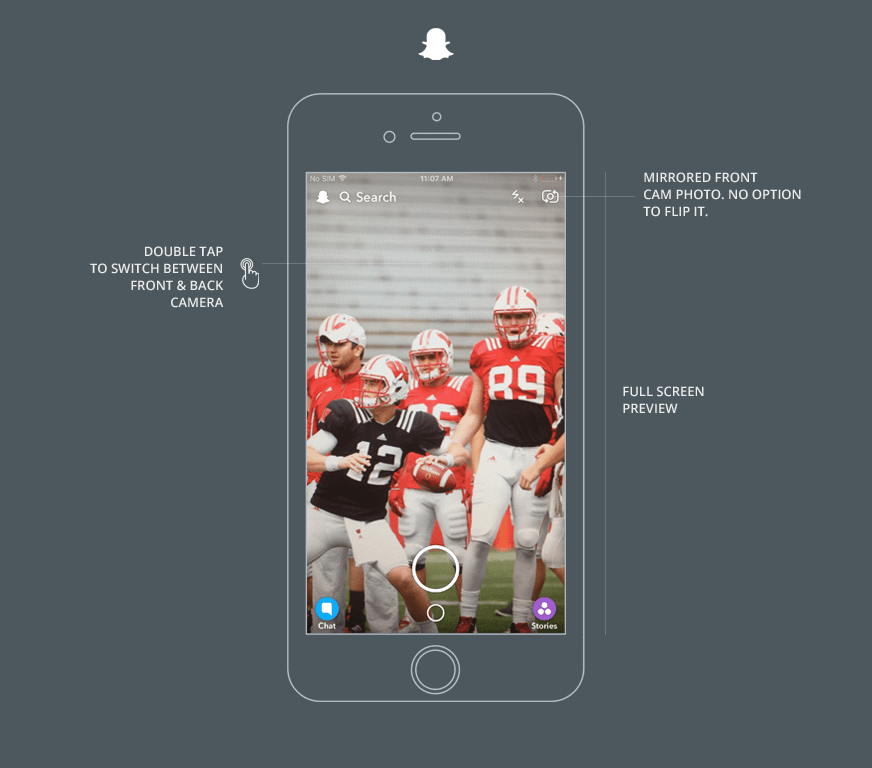
SnapChat App Camera
SnapChat accelerated the revolution in photo and video sharing by innovating with the Camera app design. The SnapChat iOS app uses a full screen camera controller view. The camera controller icons are bright and easy to see against all kinds of backgrounds. Some are filled with color and are extremely easy to see while the white icons have a black outline to allow them to stand out against light and dark backgrounds. For convenience, the front and back cameras can be switched with a double tap.
The SnapChat user experience has a few shortcomings. There is no option to flip the photo in case the front camera is used. This means the photo is always mirrored. Also there is no way to tell what the small circle below the shutter button does except to press it. It’s used to access photos from the gallery.
WhatsApp Camera
The WhatsApp iOS app uses a simple full screen camera that provides a nice, large space to take photos. There is instructional text at the bottom of the screen to help novice users. The camera controller is simple, meeting the expectations of the user while minimizing clutter or unnecessary features. Controls are placed in the lower portion of the screen, making them easy to find.
For convenience, WhatsApp uses gestures in their app design.
Pressing and holding the shutter button toggles between taking photos and recording videos. Double tapping switches between the front and back cameras. There are problems in the app design, however. There is no option to flip photos taken with the front camera- they are always mirrored. Also, the strip of gallery photos is quite inconvenient and frustrating to use, as the user has to tape and hide it each time before taking a photo.
| Feature | iOS Camera | Facebook Camera | SnapChat | ||
| Full screen Camera View | X | X | X | ||
| Front camera image can be flipped to to correct mirroring | X | X | |||
| Use of color in buttons to improve usability | X | X | |||
| Tap and hold the shutter button toggles between taking a photo and recording a video | X | X | |||
| Text interface makes the app simple to understand | X | X |
Recommendations on a Camera View for Designing Apps
How do you design apps with the perfect camera controller interface? You should focus on doing the basic things correctly without adding unnecessary bells and whistles. Here are our recommendations for the perfect camera control app based on what we have learned:
- Use the maximum screen space.
Always design apps to make use of the full screen space available. If your application uses a defined ratio or screen space, then give the user the option to crop the image after the photo is taken. - Include a way to toggle between the front and back cameras.
The user should be able to quickly toggle between the front and back cameras. This can be done by tapping on the main screen or by adding an icon for visual representation. - Use a single button for capturing photos/video.
The user should be able to switch between photo and video modes using the long press and single tap interaction. A visual indicator such as a time counter should be added to the screen to represent video recording. - Add a shadow or background to icons over the camera view.
Use a gradient background or a single-pixel shadow behind the icons in the interface to keep them visible on all kind of camera view backgrounds. When you design apps which incorporate a camera controller, test your icons by pointing your camera to light, dark and complex backgrounds. - Include a way to flip photos.
This is a common mistake made by most of the apps with a front camera view: they do not mirror the photo after it is captured which can result in odd problems. Always give the user the option to manually flip the image or flip it automatically before displaying the preview to the user. When you design apps which correct errors automatically for your users, you will make their lives easier and you will improve your chances for success.
Start a conversation by filling the form
All information will be kept confidential.
Insights
What is Serverless Architecture and how it works?
Serverless Architecture is a software design model where a third-party service hosts applications and removes the need for server hardware and software management.
Digital Transformation in Banking
Digital Transformation in Banking allows financial institutes to know what customers want and strengthen customer engagement with personalized offerings.
Impact of Cloud Computing in Healthcare Industry
Cloud Computing in healthcare sector allows care providers to store patient data on the cloud while avoiding costs of maintaining physical servers.